Introducing a new instalment to our blog: Bitvice’s Bitcoin Basics.
For those that are new to Bitcoin we will be covering the basics in a simple, bite-sized way to help you learn more about this complex subject and to give you the tools to explain the topic to friends and family in a concise manner.
This week’s topic: Bitcoin’s Blockchain.
What is Bitcoin’s Blockchain and Why is it Important?
If you have been following Bitcoin, you would have heard the term ‘blockchain’ which is the technology behind the Bitcoin network.
A blockchain is a way of recording and storing information, essentially like a database. Where blockchain differs from a traditional database is how the data is structured.
A blockchain collects sets of information in groups called blocks. These blocks have particular storage capacities and once these are filled the block is chained onto the previously filled block and this continues, creating a chain of data-filled blocks known as a blockchain.
Each block is given a timestamp of when it is added to the chain and is set in stone. This forms an irreversible timeline of data and makes the data harder to manipulate. An incredible amount of computing power would be needed to alter a single piece of data on the blockchain.
The blockchain network has a self-auditing system that guarantees the accuracy of its data by automatically verifying itself at certain intervals.
Bitcoin uses blockchain technology to store every Bitcoin transaction ever made. In Bitcoin’s case the blockchain is completely decentralized as the database is not kept in a single location and cannot be controlled by a central authority/party. It is instead hosted by tens of thousands computers all at once all across the globe. The power of this technology is its ability to distribute this information across all the nodes in the network. A node is a computer that validates the transactions on the blockchain. When a new block is added, every node (computer) updates the blockchain to show the change.
Each node has a complete record of all the Bitcoin transactions. If one node has an error in its data it can use the thousands of other nodes as a reference point to correct itself. Not one node within the network can alter information held within it and, therefore, Bitcoin’s blockchain (filled with all Bitcoin’s transactions) is irreversible. If one user tries to hack or alter the record, all other nodes would cross-reference each other and easily locate the incorrect data. This system creates an exact, transparent, chronological ledger of Bitcoin transactions.
Blockchain technology is important because it allows Bitcoin to be decentralized, transparent and secure and this adds inherent and underlying value. Bitcoin is free from any central authority and has no central point of failure. Due to its decentralised nature, it has complete global demand and thus, it has become one of the most liquid assets in the world – available in close to all countries world-wide.
To read more about Bitcoin’s underlying value you can check out our knowledge base here.
Below we will illustrate Bitcoin’s transaction process on the blockchain:
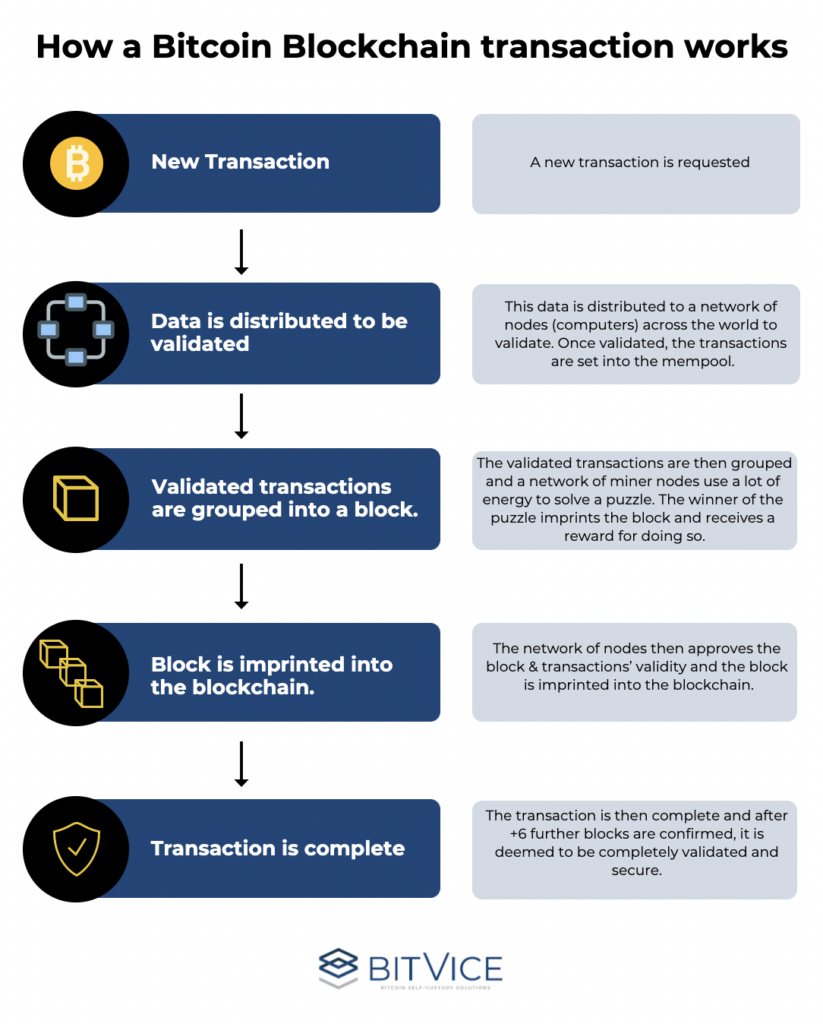
The Bitcoin space has a vast amount of information to navigate and understand. Just take it bit by bit, and stay tuned for the next instalment of Bitvice’s Bitcoin Basics.
Keep learning, keep stacking and have an awesome week.



